- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hi All,
I am getting bellow mentioned error while running update command through linked server.
OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI11» for linked server «SQLMPDB» returned message «Row handle referred to a deleted row or a row marked for deletion.».
Msg 7346, Level 16, State 2, Line 1
Cannot get the data of the row from the OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI11» for linked server «SQLMPDB».here i am using bellow mentioned update command
Update top (20000) [SQLMPDB].PSM_New_01.dbo.Trans_app_Log set INSERTFLG =’M’ from [SQLMPDB].PSM_New_01.dbo.Trans_app_Log t, [SQLMPDB].PSM_New_01.dbo.Transfer_Reg_no R where t.Reg_no=R.Reg_no and (INSERTFLG <>’M’ or INSERTFLG is NULL)
some time the above mentioned query execute successfully.most of the time we are getting error.
this command is properly running for remaining table .i am getting this issue for particular one table .i am not using any triggers in that table.
Please Help as soon as possible.
Thanks in advance…..
Regards
Ganesh
Answers
-
Since you have a dynamic server name, here is a modification to my original suggestion to use EXEC() AT, since the server name in that case cannot be a variable.
DECLARE @sp_executesql nvarchar(200) = quotename(@Source_ServerName) + ‘.’ + quotename(@Source_DatabaseName) + ‘.sys.sp_executesql’
set @UpdateStatement = ‘Update top (20000) dbo.’ + quotename(@Table_name) + ‘ set INSERTFLG =»M» from
dbo.’ + quotename(@Table_name) + ‘ t, dbo.Transfer_Reg_no R where t.Reg_no=R.Reg_no and (INSERTFLG <>»M» or INSERTFLG is NULL)’
EXEC @sp_executesql @UpdateStatementThe idea is the same as in my first post: force execution to occur on the remote server entirely and thereby avoiding the mysterious error you run into.
The key here is that EXEC accepts a variable for the procedure name, and therefore you can run sp_executesql on the remote server, and when you prefix sp_executesql with the database name, it will execute in the context of that database. This also has the
side effect of making the code easier to read.An observation: shouldn’t you have a transaction so that the UPDATE and the following INSERT is the same transaction so that the contents of the local table is guaranteed to be sync with the source table?
-
Marked as answer by
Wednesday, July 5, 2017 5:53 AM
-
Marked as answer by
Hi All,
I created a linked server in sql server to postgres database the connection was created successfully but when i try to run a query i get error
TITLE: Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
——————————
Enumerate columns failed for LinkedServer ‘PGRH’. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo)
For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server&ProdVer=10.50.1600.1+((KJ_RTM).100402-1539+)&EvtSrc=Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.ExceptionTemplates.FailedOperationExceptionText&EvtID=Enumerate+columns+LinkedServer&LinkId=20476
——————————
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
An exception occurred while executing a Transact-SQL statement or batch. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
——————————
Cannot get the data of the row from the OLE DB provider «SQL Server» for linked server «(null)». Conversion failed because the data value overflowed the data type used by the provider. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 7346)
For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server&ProdVer=10.00.1600&EvtSrc=MSSQLServer&EvtID=7346&LinkId=20476
——————————
BUTTONS:
OK
——————————
what do i do????
Dear All,
While updating he particular table i am getting this issue.
i am using sql server 2102 sp1
the update command is running through ssis package.
Update top (20000) [SQLMPDB].MPLokSewa_PSM_New_01.dbo.Trans_app_Log set INSERTFLG =’M’ from [SQLMPDB].MPLokSewa_PSM_New_01.dbo.Trans_app_Log t, [SQLMPDB].MPLokSewa_PSM_New_01.dbo.Transfer_Reg_no R where t.Reg_no=R.Reg_no and (INSERTFLG <>’M’ or INSERTFLG is NULL)
i have check with nolock also still i am getting same issue.
Please help suggest me.
Regards
Ganesh Yerme
Microsoft SQL ServerSSIS
All of life is about relationships, and EE has made a viirtual community a real community. It lifts everyone’s boat
Unlimited question asking, solutions, articles and more.
This is the best money I have ever spent. I cannot not tell you how many times these folks have saved my bacon. I learn so much from the contributors.
rwheeler23
Unlimited question asking, solutions, articles and more.
Not exactly the question you had in mind?
Sign up for an EE membership and get your own personalized solution. With an EE membership, you can ask unlimited troubleshooting, research, or opinion questions.
ask a question
Unlimited question asking, solutions, articles and more.
Experts Exchange has (a) saved my job multiple times, (b) saved me hours, days, and even weeks of work, and often (c) makes me look like a superhero! This place is MAGIC!
Walt Forbes
Friday, April 25. 2008
Setting up PostgreSQL as a Linked Server in Microsoft SQL Server 64-bit
Printer Friendly
We would like to thank Jeff Crumbley of IILogistics for providing many of these steps
and informing us that Microsoft has finally released a
64-bit OLEDB for ODBC driver.
For those who have not experienced the torture of this situation — let me start with a little background.
First if you are running SQL Server 2005 32-bit and wished to create a linked server to a PostgreSQL server, everything is hunky dory. If
however you had a SQL Server 2005 64-bit server, you ran into 2 very annoying obstacles.
- Obstacle 1: There for a long-time was no 64-bit ODBC driver nor native driver for PostgreSQL. This obstacle was somewhat alleviated
when Fuurin Kazanbai made experimental compiled 64-bit PostgreSQL ODBC drivers available which work for AMD and Intel based processors. - Obstacle 2: All looked good in the world until you tried this in SQL Server 2005 64-bit and low and behold — you needed a 64-bit OLEDB provider
for ODBC to use it in SQL Server 2005 64-bit. Yes we waited patiently for years for this piece to be available. We still love you Microsoft.
Then as Jeff Crumbley pointed out — Microsoft released an OLEDB 64-bit provider for ODBC in early April 2008.
Below are the steps to get a PostgreSQL linked server working in SQL Server 2005 64-bit.
- Run WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB948459-v2-x64-ENU.exe —
(Available as of 4/4/2008 from: http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=000364db-5e8b-44a8-b9be-ca44d18b059b&displaylang=en) (If you are running Vista 64-bit or Windows 2008 64-bit these are included already (or possibly in SP1)) - Make the folder C:Program FilesPostgreSQL8.1AMD64bin (seems to also work fine against 8.3/8.4 if you are running that) and place
the dlls from psqlodbc_AMD64 available from
http://www.geocities.jp/inocchichichi/psqlodbc/index.html
There is a newer compiled 64-bit ODBC driver at http://code.google.com/p/visionmap/wiki/psqlODBC If you are using this newer driver the use PostgreSQL 64-bit ODBC Drivers for the driver name instead of what we have below. The newere driver doesn’t seem to handle data type conversion quite as well as the older. - Run the psqlodbcwAMD64.reg file
- Create a System DSN in the 64-bit Data Source (ODBC) — alternatively you can skip this and use and embedded file DSN in
SQL Server 2005 that we will outline in the next step. - Create a Linked Server in SQL Server — below is a sample script that creates a PostgreSQL Linked Server in Microsoft SQL Server
2005 64-bit.EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NAMEOFLINKEDSERVERHERE', @srvproduct=N'PostgreSQL AMD64A', @provider=N'MSDASQL', @provstr=N'Driver=PostgreSQL AMD64A;uid=pguser;Server=pghost;database=pgdatabase;pwd=somepassword' /* For security reasons the linked server remote logins password is changed with ######## */ EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NAMEOFLINKEDSERVERHERE', @useself=N'True',@locallogin=NULL,@rmtuser=NULL,@rmtpassword=NULLAfter that you should see the linked server in SQL Server 2005 Management ->Server Objects ->Linked Server and from there
you can fiddle further with the settings. You should also be able to expand the PostgreSQL linked server and see the tables and views. - To test out the linked server — you can run the sample query below in SQL Server:
SELECT * FROM OpenQuery(NAMEOFLINKEDSERVERHERE, 'SELECT * From information_schema.tables')
Keep in mind that the PostgreSQL 64-bit ODBC is marked as experimental, but we have had good success with it on an Intel processor based
64-bit Windows 2003 running SQL Server 2005 64-bit.
Содержание статьи:
-
- SQL-сервер не найден или недоступен, ошибки соединения с SQL-сервером
- Ошибка SQL-сервера 26
- Ошибка SQL-сервера 18456
- Не удалось запустить SQL-server — код ошибки 3417
- Повреждена база данных
- Код ошибки SQL-сервера 945
- Код ошибки SQL-сервера 5172
- Ошибка SQL-сервера 823
- Ошибка SQL-сервера 8946
- Другие ошибки SQL Server
- Код ошибки SQL-сервера 1814
- Код ошибки SQL-сервера 1067
- SQL-сервер запускается, но работает слишком медленно
- SQL-сервер не найден или недоступен, ошибки соединения с SQL-сервером
SQL-сервер не найден или недоступен, ошибки соединения с SQL-сервером
- Если SQL-сервер не найден, убедитесь, что ваш экземпляр SQL-сервера действительно установлен и запущен. Для этого зайдите на компьютер, где он установлен, запустите диспетчер конфигурации SQL и проверьте, есть ли там тот экземпляр, к которому вы пытаетесь подключиться и запущен ли он. Нелишним будет также получить отчет об обнаружении компонентов SQL-серверов.
- Если вы проделали п1. и не обнаружили источник проблемы, возможно, неверно указан IP-адрес компьютера или номер порта TCP. Перепроверьте их настройки.
- Причиной того, что невозможно подключиться к SQL-серверу, также может быть сеть, убедитесь, что компьютер с SQL-сервером доступен по сети.
- Проверьте, может ли клиентское приложение, установленное на том же компьютере, что и сервер, подключиться к SQL-серверу. Запустите SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS), в диалоговом окне “Подключиться к серверу” выберите тип сервера Database Engine, укажите способ аутентификации “Аутентификация Windows”, введите имя компьютера и экземпляра SQL-сервера. Проверьте подключение.
Обратите внимание, что многие сообщения об ошибках могут быть не показаны или не содержат достаточной информации для устранения проблемы. Это сделано из соображений безопасности, чтобы при попытке взлома злоумышленники не могли получить информацию об SQL-сервере. Полные сведения содержатся в логе ошибок, который обычно хранится по адресу C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL13.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogERRORLOG, или там, куда его поместил администратор системы.
Ошибка SQL-сервера 26
Одна из наиболее часто встречающихся ошибок подключения к SQL-серверу, обычно связана с тем, что в настройках SQL-сервера не разрешены или ограничены удаленные соединения. Чтобы это исправить, попробуйте:
- в SSMS в настройках SQL-сервера включите аутентификацию Windows
- для брандмауэра Windows создайте новое правило, которое разрешает подключение для всех программ и протоколов с указанного IP-адреса
- убедитесь, что запущена служба SQL Server Browser
Ошибка SQL-сервера 18456
Эта ошибка означает, что попытка подключиться к серверу не успешна из-за проблем с именем пользователя или паролем. По коду ошибки в журнале ошибок можно узнать более точную причину, чтобы устранить ее.
Не удалось запустить SQL-server — код ошибки 3417
Возникает в случае, если были изменены настройки Windows или перемещена папка с файлами MSSQL.
- зайдите в C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQLServerMSSQL.1MSSqLData — БезопасностьНастройки доступа — Учетная запись сетевой службы — добавьте учетную запись сетевой службы
- проверьте, что MDF-файл не сжимается. Если это не так, отключите “Сжимать содержимое для экономии места на диске” в свойствах файла
Иногда ни один из этих способов не помогает, это значит, что файлы БД повреждены и ее придется восстанавливать из резервной копии.
Повреждена база данных
Код ошибки SQL-сервера 945
Ошибка 945 возникает, когда БД SQL-сервера помечена как IsShutdown. Проверьте, достаточно ли места на диске, достаточно ли прав у учетной записи для операций с БД, файлы MDF и LDF не должны быть помечены “Только для чтения”.
Код ошибки SQL-сервера 5172
SQL-сервер хранит свою физическую БД в первичном файле, в котором информация разбита постранично. Первая страница содержит информацию о заголовке mdf-файла и называется страницей заголовка. Она состоит из разнообразной информации о БД, такой как размер файла, подпись и т.д. В процессе прикрепления MDF на SQL-сервере часто возникает ошибка 5172. Это в основном происходит, если MDF-файл поврежден, информация в его заголовке тоже и соответственно сложно добраться до данных. Причиной может быть вирус, аварийное выключение системы, ошибка оборудования.
Ошибка SQL-сервера 823
SQL использует API Windows для операций ввода-вывода, но кроме завершения этих операций SQL проверяет все ошибки обращений к API. Если эти обращения несовместимы с ОС, появляется ошибка 823. Сообщение об ошибке 823 означает, что существует проблема с базовым оборудованием для хранения данных или с драйвером, который находится на пути запроса ввода-вывода. Пользователи могут столкнуться с этой ошибкой, если в файловой системе есть противоречия или поврежден файл базы данных.
Ошибка SQL-сервера 8946
Основной причиной ошибки 8946 так же, как и для 5172, является повреждение заголовков страниц БД SQL вследствие сбоя питания, вирусной атаки, отказа оборудования — SQL-сервер больше не может прочесть эти страницы.
Перечисленные ошибки 945, 5172, 823, 8946 можно устранить двумя методами:
- если у вас есть свежая резервная копия базы — восстановить базу из этой копии
- можно попробовать использовать специализированное ПО, такое как SQL Recovery Tool, чтобы восстановить поврежденные файлы
Желательно определить, что именно привело к возникновению ошибок и принять меры, чтобы это не повторялось — заменить плохо работающее оборудование, повысить информационную безопасность.
Другие ошибки SQL
Код ошибки SQL-сервера 1814
SQL-сервер не может создать базу данных tempdb. Убедитесь, что на выделенном под нее диске достаточно места и что у учетной записи хватает прав для записи в указанную директорию.
Код ошибки SQL-сервера 1067
Эта ошибка может возникать по разным причинам. Наиболее часто оказывается, что повреждены или отсутствуют конфигурационные файлы, SQL-сервер обращается к поврежденным системным файлам, ошибочные данные пользователя, нет информации про лицензию. В самых тяжелых случаях придется переустанавливать SQL-сервер. Но иногда помогает восстановление поврежденных файлов или изменение настроек SQL-сервера — вы можете создать новую учетную запись в домене и использовать ее для службы MSSQL.
SQL-сервер запускается, но работает слишком медленно
Проанализируйте журнал сервера, индексы (фрагментацию), запросы, задания, возможность взаимных блокировок. Причин может быть масса.
Мы работаем с разными версиями SQL-сервера уже много лет, знакомы со всевозможными инструкциями SQL-сервера, видели самые разные варианты его настройки и использования на проектах у своих клиентов. В целом мы можем выделить четыре основных источника неполадок:
- Индексы — причина проблем номер один. Неправильные индексы, отсутствующие индексы, слишком много индексов и подобное. Чаще всего при проблеме с индексами пользователи или администраторы базы данных не получают сообщения об ошибке, они просто видят, что база работает очень медленно и докопаться до причин бывает очень нелегко
- изначально плохая архитектура сервера баз данных — ошибка, которую очень сложно и дорого исправлять на этапе, когда база уже используется
- плохой код, в котором возможны блокировки и тупиковые места
- использование конфигурации по умолчанию,
Если у вас не получается устранить ошибки сервера SQL-server самостоятельно, если они появляются снова и снова, то скорее всего в основе лежит одна из этих причин. В таком случае — если у вас произошла ошибка с SQL сервером, ваше ПО не видит SQL-сервер, либо нужно развернуть кластер SQL-серверов — вы всегда можете обратиться за консультацией и технической поддержкой к специалистам Интегруса, отправив заявку с сайта, написав на e-mail, либо позвонив в колл-центр нашей компании.

Присоединяйтесь к нам,
чтобы получать чек-листы, реальные кейсы, а также
обзоры сервисов раз в 2 недели.
Summary: As an SQL user, you may come across a situation when attempting to start the SQL Server results in SQL error 3417. This blog discusses different occurrences of the error and causes behind it. Also, the blog explores workarounds on how to resolve SQL Server Error 3417. You can troubleshoot the error manually or by using a SQL repair tool.

Contents
- Occurrences of SQL Error 3417
- What Causes SQL Server Error 3417?
- How to Fix SQL Server Error 3417?
- Conclusion
Sometimes, when trying to start SQL Server service manually, SQL Server error 3417 may occur. The complete error message reads as:
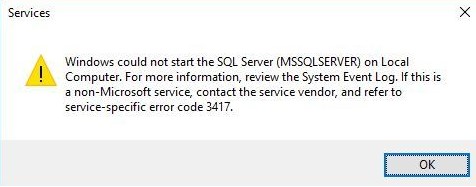
“Windows could not start the SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER) on Local Computer. For more information, review the System Event Log. If this is a non-Microsoft service, contact the service vendor, and refer to service-specific error code 3417.”
Before discussing the reasons behind the SQL service error 3417 and workarounds to fix it, let’s first look at a few user instances reporting the error.
Occurrences of SQL Error 3417
Instance 1: In this instance, a user reported that when moving the folder: (Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL11.MSSQLSERVERMSSQL) to another drive, the SQL server stopped working. On trying to start the server again, it displayed an error message: “Windows could not start the SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER) on Local Computer. For more information, review the System Event Log. If this is a non-Microsoft service, contact the service vendor, and refer to service-specific error code 3417.”
Instance 2: When trying to connect to SQL Server to run a web project, a user received an error message: “A network-related or instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connection to SQL Server. The server was not found or was not accessible. Verify that the instance name is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections. (provider: SQL Network Interfaces, error: 40 – Error Locating Server/Instance Specified)”
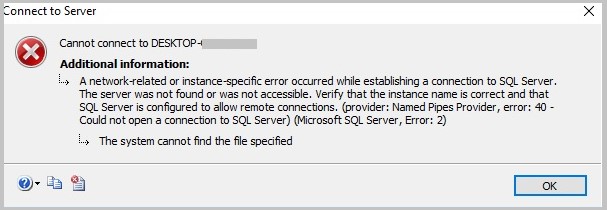
The user found that SQL Server Express stopped working in SQL Server Configuration Manager. On attempting to run SQL Server Express, the service did not respond. And when the user tried opening services.msc to start a SQL Server (SQLEXPRESS instance), it returned the “Windows could not start the SQL Server (SQLEXPRESS) on local computer” error message with error code 3417.
What Causes SQL Server Error 3417?
You may encounter this error when the SQL Server doesn’t start due to any of these reasons:
- “Master database or tempdb cannot be brought online.” This event may occur when the db is damaged due to hardware or software failure.
- The folder containing the MDF and NDF files is compressed.
- Folder permission issue where the db file resides.
Tip: SQL Server error 3417 can render the SQL database inaccessible. While there are manual workarounds, troubleshooting using these workarounds can take significant time and increase db downtime. Use a SQL repair tool to restore the db in a few simple clicks.
How to Fix SQL Server Error 3417?
Try the following workarounds in the sequence given below to resolve MS SQL error 3417:
Workaround 1: Decompress SQL Database MDF File
When you cannot open the master database, check if the master database file (.mdf) is compressed. If the file is compressed, you will need to decompress it. To do so, follow these steps:
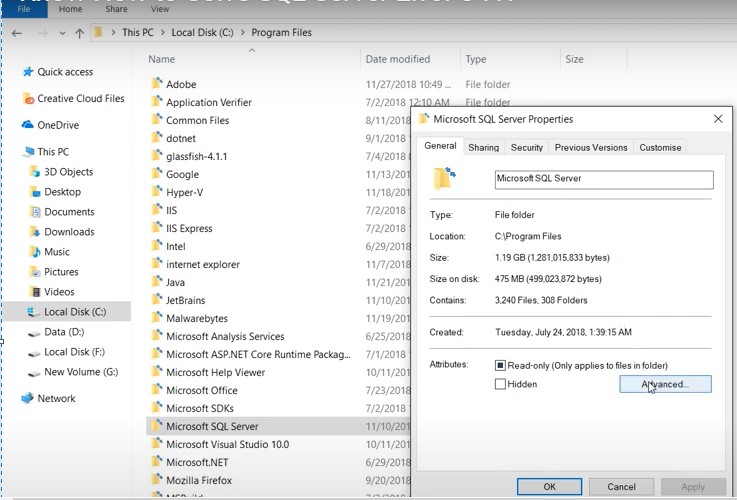
Step 1: Browse and locate the Microsoft SQL Server data folder containing db (MDF and NDF) files.
Note: You can locate the SQL server data folder by browsing the location: “C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL.1MSSQLData”.
Step 2: Right-click on the SQL Server data folder. The Microsoft SQL Server Properties window gets displayed. Click Advanced.
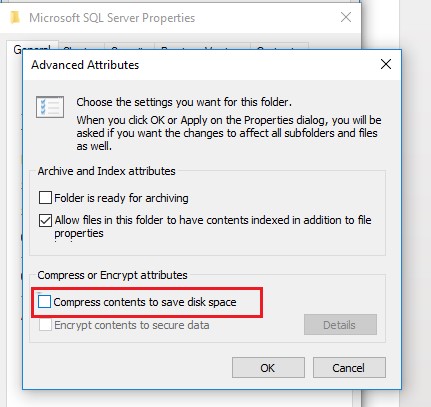
Step 3: In the Advanced Attributes dialog box that appears, uncheck the Compress contents to save disk space checkbox, and then click OK.
Step 4: The Microsoft SQL Server Properties dialog box opens again. Click on the Apply button, and then hit OK. When the Confirm Attribute Changes box pops-up, click OK.
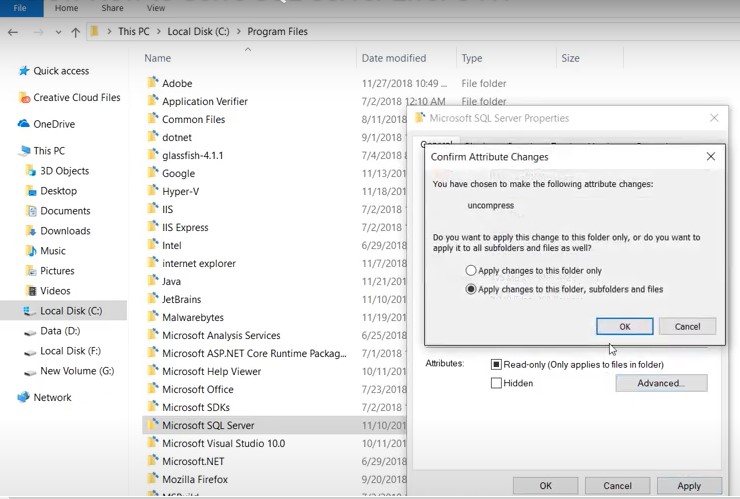
Step 5: Click Continue to proceed.
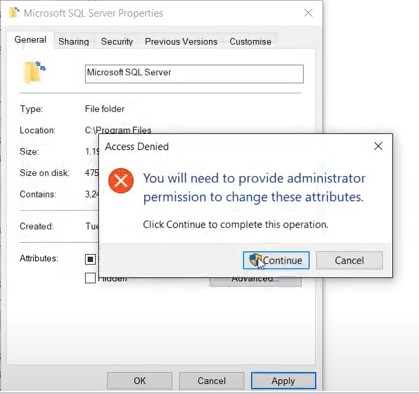
Step 6: Wait for the attribute changes to complete. Once the changes have been applied, click OK.

After performing these steps, try starting the SQL Server service again. If the error persists, proceed with the next workaround.
Workaround 2: Check for Folder Permissions
Note: This SQL error 3417 fix applies to users who receive the error while moving a folder to another drive.
Make sure that the account that runs the SQL Server service has access rights (network permissions) to the folder containing the SQL db files. If not, follow these steps to grant the right to the folder:
Step 1: Go to the SQL files folder and right-click on it, and then choose Properties.
Step 2: From the Properties box, click the Security tab.
Step 3: In the dialog box that pops-up, choose the Network Service account under the Group or user names: section.
Step 4: Select the Full control checkbox under the Permissions for Authenticated Users section, and hit the OK button.
Now check if running the SQL Server instance starts without the error.
Workaround 3: Rebuild Master Database
We can restore master db from the most recent full database backup, but only if the SQL Server instance is running. Since we cannot start the server instance, rebuilding the master db might help fix the 3417 error.
Refer to this link for more information on rebuilding the master database.
Workaround 4: Repair MDF File
If rebuilding the master db doesn’t help resolve the error, the chances are that the master db file is severely corrupt. In that case, you can try to repair the corrupted MDF file. For more information on repairing the db file, read this: Repairing Corrupt MDF File of SQL Server Database.
Conclusion
You may encounter SQL Server error 3417 when trying to start the SQL Server service. The error may occur when you cannot bring online the master or tempdb, the folder containing the database (.mdf or .ndf) files is compressed, or you don’t have access rights on the folder. You can try to resolve the issue by following the manual workarounds discussed in this post. However, troubleshooting SQL error 3417 manually can be time-consuming and increases database downtime. A better approach is to use a specialized SQL database repair tool such as Stellar Repair for MS SQL to repair the MDF file and fix the error.
About The Author
Charanjeet
Charanjeet is a Technical Content Writer at Stellar®who specializes in writing about databases, e-mail recovery, and e-mail migration solutions. She loves researching and developing content that helps database administrators, organizations and novices to fix multiple problems related to MS SQL and MySQL databases and Microsoft Exchange.
Best Selling Products

Stellar Repair for MS SQL
Stellar Repair for MS SQL is an enterpri
Read More
![]()
Stellar Toolkit for MS SQL
3-in-1 software package, recommended by
Read More

Stellar Converter for Database
Stellar Converter for Database is an eff
Read More

Stellar Repair for Access
Powerful tool, widely trusted by users &
Read More
Microsoft SQL Server Ошибки
Useful links
- System Error Messages
- Database Engine Error Severities
- Integration Services Error and Message Reference
- View and Read SQL Server Setup Log Files
- Troubleshoot the SQL Server Utility
- Common Issues: Licensing Errors
- SQL Server 2016 Distributed Replay Errors
- The Instance ID MSSQLSERVER Is Already In Use
- SQL Server: Detach/Attach Gotchas!
SQL Server All Errors List
SELECT message_id, severity, text
FROM sys.messages
WHERE language_id = 1033; /* assuming US English */Your language_id you can find in
sys.syslanguages
system view, column msglangid:
| langid | dateformat | datefirst | upgrade | name | alias | months | shortmonths | days | lcid | msglangid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | mdy | 7 | 0 | us_english | English | January,February,March,April,May,June,July,August,September,October,November,December | Jan,Feb,Mar,Apr,May,Jun,Jul,Aug,Sep,Oct,Nov,Dec | Monday,Tuesday,Wednesday,Thursday,Friday,Saturday,Sunday | 1033 | 1033 |
| 1 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Deutsch | German | Januar,Februar,März,April,Mai,Juni,Juli,August,September,Oktober,November,Dezember | Jan,Feb,Mär,Apr,Mai,Jun,Jul,Aug,Sep,Okt,Nov,Dez | Montag,Dienstag,Mittwoch,Donnerstag,Freitag,Samstag,Sonntag | 1031 | 1031 |
| 2 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Français | French | janvier,février,mars,avril,mai,juin,juillet,août,septembre,octobre,novembre,décembre | janv,févr,mars,avr,mai,juin,juil,août,sept,oct,nov,déc | lundi,mardi,mercredi,jeudi,vendredi,samedi,dimanche | 1036 | 1036 |
| 3 | ymd | 7 | 0 | 日本語 | Japanese | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 月曜日,火曜日,水曜日,木曜日,金曜日,土曜日,日曜日 | 1041 | 1041 |
| 4 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Dansk | Danish | januar,februar,marts,april,maj,juni,juli,august,september,oktober,november,december | jan,feb,mar,apr,maj,jun,jul,aug,sep,okt,nov,dec | mandag,tirsdag,onsdag,torsdag,fredag,lørdag,søndag | 1030 | 1030 |
| 5 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Español | Spanish | Enero,Febrero,Marzo,Abril,Mayo,Junio,Julio,Agosto,Septiembre,Octubre,Noviembre,Diciembre | Ene,Feb,Mar,Abr,May,Jun,Jul,Ago,Sep,Oct,Nov,Dic | Lunes,Martes,Miércoles,Jueves,Viernes,Sábado,Domingo | 3082 | 3082 |
| 6 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Italiano | Italian | gennaio,febbraio,marzo,aprile,maggio,giugno,luglio,agosto,settembre,ottobre,novembre,dicembre | gen,feb,mar,apr,mag,giu,lug,ago,set,ott,nov,dic | lunedì,martedì,mercoledì,giovedì,venerdì,sabato,domenica | 1040 | 1040 |
| 7 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Nederlands | Dutch | januari,februari,maart,april,mei,juni,juli,augustus,september,oktober,november,december | jan,feb,mrt,apr,mei,jun,jul,aug,sep,okt,nov,dec | maandag,dinsdag,woensdag,donderdag,vrijdag,zaterdag,zondag | 1043 | 1043 |
| 8 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Norsk | Norwegian | januar,februar,mars,april,mai,juni,juli,august,september,oktober,november,desember | jan,feb,mar,apr,mai,jun,jul,aug,sep,okt,nov,des | mandag,tirsdag,onsdag,torsdag,fredag,lørdag,søndag | 2068 | 2068 |
| 9 | dmy | 7 | 0 | Português | Portuguese | janeiro,fevereiro,março,abril,maio,junho,julho,agosto,setembro,outubro,novembro,dezembro | jan,fev,mar,abr,mai,jun,jul,ago,set,out,nov,dez | segunda-feira,terça-feira,quarta-feira,quinta-feira,sexta-feira,sábado,domingo | 2070 | 2070 |
| 10 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Suomi | Finnish | tammikuuta,helmikuuta,maaliskuuta,huhtikuuta,toukokuuta,kesäkuuta,heinäkuuta,elokuuta,syyskuuta,lokakuuta,marraskuuta,joulukuuta | tammi,helmi,maalis,huhti,touko,kesä,heinä,elo,syys,loka,marras,joulu | maanantai,tiistai,keskiviikko,torstai,perjantai,lauantai,sunnuntai | 1035 | 1035 |
| 11 | ymd | 1 | 0 | Svenska | Swedish | januari,februari,mars,april,maj,juni,juli,augusti,september,oktober,november,december | jan,feb,mar,apr,maj,jun,jul,aug,sep,okt,nov,dec | måndag,tisdag,onsdag,torsdag,fredag,lördag,söndag | 1053 | 1053 |
| 12 | dmy | 1 | 0 | čeština | Czech | leden,únor,březen,duben,květen,červen,červenec,srpen,září,říjen,listopad,prosinec | I,II,III,IV,V,VI,VII,VIII,IX,X,XI,XII | pondělí,úterý,středa,čtvrtek,pátek,sobota,neděle | 1029 | 1029 |
| 13 | ymd | 1 | 0 | magyar | Hungarian | január,február,március,április,május,június,július,augusztus,szeptember,október,november,december | jan,febr,márc,ápr,máj,jún,júl,aug,szept,okt,nov,dec | hétfő,kedd,szerda,csütörtök,péntek,szombat,vasárnap | 1038 | 1038 |
| 14 | dmy | 1 | 0 | polski | Polish | styczeń,luty,marzec,kwiecień,maj,czerwiec,lipiec,sierpień,wrzesień,październik,listopad,grudzień | I,II,III,IV,V,VI,VII,VIII,IX,X,XI,XII | poniedziałek,wtorek,środa,czwartek,piątek,sobota,niedziela | 1045 | 1045 |
| 15 | dmy | 1 | 0 | română | Romanian | ianuarie,februarie,martie,aprilie,mai,iunie,iulie,august,septembrie,octombrie,noiembrie,decembrie | Ian,Feb,Mar,Apr,Mai,Iun,Iul,Aug,Sep,Oct,Nov,Dec | luni,marţi,miercuri,joi,vineri,sîmbătă,duminică | 1048 | 1048 |
| 16 | ymd | 1 | 0 | hrvatski | Croatian | siječanj,veljača,ožujak,travanj,svibanj,lipanj,srpanj,kolovoz,rujan,listopad,studeni,prosinac | sij,vel,ožu,tra,svi,lip,srp,kol,ruj,lis,stu,pro | ponedjeljak,utorak,srijeda,četvrtak,petak,subota,nedjelja | 1050 | 1050 |
| 17 | dmy | 1 | 0 | slovenčina | Slovak | január,február,marec,apríl,máj,jún,júl,august,september,október,november,december | I,II,III,IV,V,VI,VII,VIII,IX,X,XI,XII | pondelok,utorok,streda,štvrtok,piatok,sobota,nedeľa | 1051 | 1051 |
| 18 | dmy | 1 | 0 | slovenski | Slovenian | januar,februar,marec,april,maj,junij,julij,avgust,september,oktober,november,december | jan,feb,mar,apr,maj,jun,jul,avg,sept,okt,nov,dec | ponedeljek,torek,sreda,četrtek,petek,sobota,nedelja | 1060 | 1060 |
| 19 | dmy | 1 | 0 | ελληνικά | Greek | Ιανουαρίου,Φεβρουαρίου,Μαρτίου,Απριλίου,Μα_ου,Ιουνίου,Ιουλίου,Αυγούστου,Σεπτεμβρίου,Οκτωβρίου,Νοεμβρίου,Δεκεμβρίου | Ιαν,Φεβ,Μαρ,Απρ,Μαϊ,Ιουν,Ιουλ,Αυγ,Σεπ,Οκτ,Νοε,Δεκ | Δευτέρα,Τρίτη,Τετάρτη,Πέμπτη,Παρασκευή,Σάββατο,Κυριακή | 1032 | 1032 |
| 20 | dmy | 1 | 0 | български | Bulgarian | януари,февруари,март,април,май,юни,юли,август,септември,октомври,ноември,декември | януари,февруари,март,април,май,юни,юли,август,септември,октомври,ноември,декември | понеделник,вторник,сряда,четвъртък,петък,събота,неделя | 1026 | 1026 |
| 21 | dmy | 1 | 0 | русский | Russian | Январь,Февраль,Март,Апрель,Май,Июнь,Июль,Август,Сентябрь,Октябрь,Ноябрь,Декабрь | янв,фев,мар,апр,май,июн,июл,авг,сен,окт,ноя,дек | понедельник,вторник,среда,четверг,пятница,суббота,воскресенье | 1049 | 1049 |
| 22 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Türkçe | Turkish | Ocak,Şubat,Mart,Nisan,Mayıs,Haziran,Temmuz,Ağustos,Eylül,Ekim,Kasım,Aralık | Oca,Şub,Mar,Nis,May,Haz,Tem,Ağu,Eyl,Eki,Kas,Ara | Pazartesi,Salı,Çarşamba,Perşembe,Cuma,Cumartesi,Pazar | 1055 | 1055 |
| 23 | dmy | 1 | 0 | British | British English | January,February,March,April,May,June,July,August,September,October,November,December | Jan,Feb,Mar,Apr,May,Jun,Jul,Aug,Sep,Oct,Nov,Dec | Monday,Tuesday,Wednesday,Thursday,Friday,Saturday,Sunday | 2057 | 1033 |
| 24 | dmy | 1 | 0 | eesti | Estonian | jaanuar,veebruar,märts,aprill,mai,juuni,juuli,august,september,oktoober,november,detsember | jaan,veebr,märts,apr,mai,juuni,juuli,aug,sept,okt,nov,dets | esmaspäev,teisipäev,kolmapäev,neljapäev,reede,laupäev,pühapäev | 1061 | 1061 |
| 25 | ymd | 1 | 0 | latviešu | Latvian | janvāris,februāris,marts,aprīlis,maijs,jūnijs,jūlijs,augusts,septembris,oktobris,novembris,decembris | jan,feb,mar,apr,mai,jūn,jūl,aug,sep,okt,nov,dec | pirmdiena,otrdiena,trešdiena,ceturtdiena,piektdiena,sestdiena,svētdiena | 1062 | 1062 |
| 26 | ymd | 1 | 0 | lietuvių | Lithuanian | sausis,vasaris,kovas,balandis,gegužė,birželis,liepa,rugpjūtis,rugsėjis,spalis,lapkritis,gruodis | sau,vas,kov,bal,geg,bir,lie,rgp,rgs,spl,lap,grd | pirmadienis,antradienis,trečiadienis,ketvirtadienis,penktadienis,šeštadienis,sekmadienis | 1063 | 1063 |
| 27 | dmy | 7 | 0 | Português (Brasil) | Brazilian | Janeiro,Fevereiro,Março,Abril,Maio,Junho,Julho,Agosto,Setembro,Outubro,Novembro,Dezembro | Jan,Fev,Mar,Abr,Mai,Jun,Jul,Ago,Set,Out,Nov,Dez | Segunda-Feira,Terça-Feira,Quarta-Feira,Quinta-Feira,Sexta-Feira,Sábado,Domingo | 1046 | 1046 |
| 28 | ymd | 7 | 0 | 繁體中文 | Traditional Chinese | 一月,二月,三月,四月,五月,六月,七月,八月,九月,十月,十一月,十二月 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 星期一,星期二,星期三,星期四,星期五,星期六,星期日 | 1028 | 1028 |
| 29 | ymd | 7 | 0 | 한국어 | Korean | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 월요일,화요일,수요일,목요일,금요일,토요일,일요일 | 1042 | 1042 |
| 30 | ymd | 7 | 0 | 简体中文 | Simplified Chinese | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 01,02,03,04,05,06,07,08,09,10,11,12 | 星期一,星期二,星期三,星期四,星期五,星期六,星期日 | 2052 | 2052 |
| 31 | dmy | 1 | 0 | Arabic | Arabic | Muharram,Safar,Rabie I,Rabie II,Jumada I,Jumada II,Rajab,Shaaban,Ramadan,Shawwal,Thou Alqadah,Thou Alhajja | Jan,Feb,Mar,Apr,May,Jun,Jul,Aug,Sep,Oct,Nov,Dec | Monday,Tuesday,Wednesday,Thursday,Friday,Saturday,Sunday | 1025 | 1025 |
| 32 | dmy | 7 | 0 | ไทย | Thai | มกราคม,กุมภาพันธ์,มีนาคม,เมษายน,พฤษภาคม,มิถุนายน,กรกฎาคม,สิงหาคม,กันยายน,ตุลาคม,พฤศจิกายน,ธันวาคม | ม.ค.,ก.พ.,มี.ค.,เม.ย.,พ.ค.,มิ.ย.,ก.ค.,ส.ค.,ก.ย.,ต.ค.,พ.ย.,ธ.ค. | จันทร์,อังคาร,พุธ,พฤหัสบดี,ศุกร์,เสาร์,อาทิตย์ | 1054 | 1054 |
| 33 | dmy | 1 | 0 | norsk (bokmål) | Bokmål | januar,februar,mars,april,mai,juni,juli,august,september,oktober,november,desember | jan,feb,mar,apr,mai,jun,jul,aug,sep,okt,nov,des | mandag,tirsdag,onsdag,torsdag,fredag,lørdag,søndag | 1044 | 1044 |
Levels of Severity
| Severity level | Description |
|---|---|
| 0-9 | Informational messages that return status information or report errors that are not severe. The Database Engine does not raise system errors with severities of 0 through 9. |
| 10 | Informational messages that return status information or report errors that are not severe. For compatibility reasons, the Database Engine converts severity 10 to severity 0 before returning the error information to the calling application. |
| 11-16 | Indicate errors that can be corrected by the user. |
| 11 | Indicates that the given object or entity does not exist. |
| 12 | A special severity for queries that do not use locking because of special query hints. In some cases, read operations performed by these statements could result in inconsistent data, since locks are not taken to guarantee consistency. |
| 13 | Indicates transaction deadlock errors. |
| 14 | Indicates security-related errors, such as permission denied. |
| 15 | Indicates syntax errors in the Transact-SQL command. |
| 16 | Indicates general errors that can be corrected by the user. |
| 17-19 | Indicate software errors that cannot be corrected by the user. Inform your system administrator of the problem. |
| 17 | Indicates that the statement caused SQL Server to run out of resources (such as memory, locks, or disk space for the database) or to exceed some limit set by the system administrator. |
| 18 | Indicates a problem in the Database Engine software, but the statement completes execution, and the connection to the instance of the Database Engine is maintained. The system administrator should be informed every time a message with a severity level of 18 occurs. |
| 19 | Indicates that a nonconfigurable Database Engine limit has been exceeded and the current batch process has been terminated. Error messages with a severity level of 19 or higher stop the execution of the current batch. Severity level 19 errors are rare and must be corrected by the system administrator or your primary support provider. Contact your system administrator when a message with a severity level 19 is raised. Error messages with a severity level from 19 through 25 are written to the error log. |
| 20-24 | Indicate system problems and are fatal errors, which means that the Database Engine task that is executing a statement or batch is no longer running. The task records information about what occurred and then terminates. In most cases, the application connection to the instance of the Database Engine may also terminate. If this happens, depending on the problem, the application might not be able to reconnect. Error messages in this range can affect all of the processes accessing data in the same database and may indicate that a database or object is damaged. Error messages with a severity level from 19 through 24 are written to the error log. |
| 20 | Indicates that a statement has encountered a problem. Because the problem has affected only the current task, it is unlikely that the database itself has been damaged. |
| 21 | Indicates that a problem has been encountered that affects all tasks in the current database, but it is unlikely that the database itself has been damaged. |
| 22 | Indicates that the table or index specified in the message has been damaged by a software or hardware problem. Severity level 22 errors occur rarely. If one occurs, run DBCC CHECKDB to determine whether other objects in the database are also damaged. The problem might be in the buffer cache only and not on the disk itself. If so, restarting the instance of the Database Engine corrects the problem. To continue working, you must reconnect to the instance of the Database Engine; otherwise, use DBCC to repair the problem. In some cases, you may have to restore the database. If restarting the instance of the Database Engine does not correct the problem, then the problem is on the disk. Sometimes destroying the object specified in the error message can solve the problem. For example, if the message reports that the instance of the Database Engine has found a row with a length of 0 in a nonclustered index, delete the index and rebuild it. |
| 23 | Indicates that the integrity of the entire database is in question because of a hardware or software problem. Severity level 23 errors occur rarely. If one occurs, run DBCC CHECKDB to determine the extent of the damage. The problem might be in the cache only and not on the disk itself. If so, restarting the instance of the Database Engine corrects the problem. To continue working, you must reconnect to the instance of the Database Engine; otherwise, use DBCC to repair the problem. In some cases, you may have to restore the database. |
| 24 | Indicates a media failure. The system administrator may have to restore the database. You may also have to call your hardware vendor. |
SQL Server Errors
| message_id | Description | Article |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | You may see “out of user memory quota” message in errorlog when you use In-Memory OLTP feature … | Out of user memory quota |
| 0 | Logon Failure: The User has not Been Granted. The operating system returned the error ????? while … | Compressed backup errors |
| 0 | A transport-level error has occurred when receiving results from the server. | link1 |
| 0 | The MSSQLSERVER service was unable to log on as SQLAuthoritySQLFarmService with the currently c … | The User has not Been Granted |
| 0 | A server error occurred on current command. The results, if any, should be discarded. | Who owns your availability groups? |
| 0 | A network-related issue or instance-specific error occured while establishing a connection to SQL Server | Cannot Connect to SQL Server |
| 0 | Connecting to Azure SQL Database: Requested tenant identifier ‘00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000’ is… | Requested tenant identifier |
| 102 | Incorrect syntax near ‘%.*ls’. | 102_link1,102_link2 |
| 120 | The select list for the INSERT statement contains fewer items than the insert list. The number of … | 120_link1 |
| 121 | The select list for the INSERT statement contains more items than the insert list. The number of … | 121_link1 |
| 131 | The size (%d) given to the %S_MSG ‘%.*ls’ exceeds the maximum allowed for any data type (%d). | 131_link1 |
| 145 | ORDER BY items must appear in the select list if SELECT DISTINCT is specified. | 145_link1 |
| 156 | Incorrect syntax near the keyword ‘ORDER’. | 156_link1 |
| 207 | Invalid column name ‘%.*ls’. | 207_link1 |
| 213 | Column name or number of supplied values does not match table definition. | 213_link1,213_link2 |
| 229 | The %ls permission was denied on the object ‘%.ls’, database ‘%.ls’, schema ‘%.*ls’. | 229_link1 |
| 241 | Conversion failed when converting date and/or time from character string. | 241_link1 |
| 257 | Implicit conversion from data type %ls to %ls is not allowed. Use the CONVERT function to run this query | 257_link1 |
| 264 | The column name ‘%.*ls’ is specified more than once in the SET clause or column list of an INSERT … | 264_link1 |
| 297 | The user does not have permission to perform this action. | 297_link1 |
| 352 | The table-valued parameter «%.*ls» must be declared with the READONLY option. | 352_link1 |
| 459 | Collation ‘%.*ls’ is supported on Unicode data types only and cannot be applied to char, varchar or … | 459_link1 |
| 535 | The datediff function resulted in an overflow. The number of dateparts separating two date/time | 535_link1 |
| 596 | Cannot continue execution because the session is in the kill state. | 596_link1,596_link2,596_link3 |
| 650 | You can only specify the READPAST lock in the READ COMMITTED or REPEATABLE READ isolation levels. | 650_link1 |
| 657 | Could not disable support for increased partitions in database … | 657_link1 |
| 666 | The maximum system-generated unique value for a duplicate group was exceeded for index with … | 666_link1 |
| 701 | There is insufficient system memory in resource pool ‘%ls’ to run this query. … | 701_link1,701_link2 |
| 824 | SQL Server detected a logical consistency-based I/O error … | 824_link1,824_link2,KB2152734,824_link3 |
| 825 | The operating system returned error %ls to SQL Server. It failed creating event for a %S_MSG at … | 825_link1 |
| 913 | Could Not Find Database %d. Database May Not be Activated Yet or May be in Transition … | 913_link1 |
| 922 | Database ‘%.*ls’ is being recovered. Waiting until recovery is finished. | 922_link1 |
| 926 | Database ‘%.*ls’ cannot be opened. It has been marked SUSPECT by recovery. See the SQL Server errorlog … | 926_link1 |
| 1052 | Conflicting %ls options «%ls» and «%ls». | 1052_link1 |
| 1065 | The NOLOCK and READUNCOMMITTED lock hints are not allowed for target tables of INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE … | 1065_link1 |
| 1105 | Could not allocate space for object ‘%.ls’%.ls in database ‘%.ls’ because the ‘%.ls’ filegroup is … | 1105_link1 |
| 1204 | The instance of the SQL Server Database Engine cannot obtain a LOCK resource at this time. Rerun your … | 1204_link1 |
| 1205 | Transaction (Process ID %d) was deadlocked on %.*ls resources with another process and has been chosen … | 1205_link1 |
| 1222 | Lock request time out period exceeded. | 1222_link1 |
| 1219 | Your session has been disconnected because of a high priority DDL operation. | 1219_link1 |
| 1480 | The %S_MSG database «%.*ls» is changing roles from «%ls» to «%ls» because the mirroring session or … | 1480_link1 |
| 1701 | Creating or altering table %ls failed because the minimum row size would be 8061, including 10 b … | 1701_link1 |
| 1807 | Could not obtain exclusive lock on database ‘model’. Retry the operation later. … | 1807_link1 |
| 1904 | The statistics on table has 65 columns in the key list … | 1904_link1 |
| 1908 | Column ‘%.ls’ is partitioning column of the index ‘%.ls’. Partition columns for a unique index … | 1908_link1 |
| 2533 | Table error: page %S_PGID allocated to object ID %d, index ID %d, partition ID %I64d, alloc unit ID … | 2533_link1 |
| 2534 | Table error: page %S_PGID, whose header indicates that it is allocated to object ID %d, index ID %d, … | 2534_link1 |
| 2812 | Could not find stored procedure ‘%.*ls’. | 2812_link1 |
| 3101 | Exclusive access could not be obtained because the database is in use. … | 3101_link1 |
| 3154 | The backup set holds a backup of a database other than the existing … | 3154_link1 |
| 3241 | The media family on device ‘%ls’ is incorrectly formed. SQL Server cannot process this media fam … | 3241_link1 |
| 3314 | During undoing of a logged operation in database ‘%.*ls’, an error occurred at log record ID %S … | 3314_link1 |
| 3634 | The operating system returned the error ‘%ls’ while attempting ‘%ls’ on ‘%ls’. … | 3634_link1 |
| 3637 | A parallel operation cannot be started from a DAC connection. | 3637_link1 |
| 3743 | The database ‘%.*ls’ is enabled for database mirroring. Database mirroring must be removed befor … | 3743_link1 |
| 3906 | Failed to update database «%.*ls» because the database is read-only. | 3906_link1 |
| 3930 | The current transaction cannot be committed and cannot support operations that write to the log … | 3930_link1 |
| 3956 | Snapshot isolation transaction failed to start in database ‘%.*ls’ because the ALTER DATABASE command … | 3956_link1 |
| 3960 | Snapshot isolation transaction aborted due to update conflict. You cannot use snapshot isolation to … | 3960_link1 |
| 4064 | Cannot open user default database. Login failed.Login failed. … | 4064_link1 |
| 4189 | Cannot convert to text/ntext or collate to ‘%.*ls’ because these legacy LOB types do not support UTF-8 … | 4189_link1 |
| 4353 | Conflicting file relocations have been specified for file ‘%.*ls’. Only a single WITH MOVE clause … | 4353_link1 |
| 4629 | Permissions on server scoped catalog views or system stored procedures or extended stored … | 4629_link1 |
| 4901 | ALTER TABLE only allows columns to be added that can contain nulls, or have a DEFAULT definition … | 4901_link1 |
| 4922 | ALTER TABLE ALTER COLUMN Address failed because one or more objects access this column. … | 4922_link1 |
| 4934 | Computed column ‘%.ls’ in table ‘%.ls’ cannot be persisted because the column does user or … | 4934_link1 |
| 4947 | ALTER TABLE SWITCH statement failed. There is no identical index in source table ‘%.*ls’ for the … | 4947_link1 |
| 5004 | To use ALTER DATABASE, the database must be in a writable state in which a checkpoint can be executed. | 5004_link1 |
| 5011 | User does not have permission to alter database ‘%.*ls’, the database does not exist, or the database … | 5011_link1 |
| 5061 | ALTER DATABASE failed because a lock could not be placed on database ‘%.*ls’. Try again later. | 5061_link1 |
| 5084 | Setting database option %ls to %ls for database ‘%.*ls’. | 5084_link1 |
| 5120 | Unable to open the physical file … Operating system error 5: «5(Access is denied.)» … | SQL SERVER — FIX Error 5120 |
| 5123 | CREATE FILE encountered operating system error «%ls»(The system cannot find the path specified.) … | 5123_link1, 5123_link2 |
| 5171 | %.*ls is not a primary database file. | 5171_link1 |
| 5172 | The header for file ‘%ls’ is not a valid database file header. The %ls property is incorrect. | 5172_link1 |
| 5235 | %lsDBCC %ls (%ls%ls%ls)%ls executed by %ls terminated abnormally due to error state %d. Elapsed time: … | 5235_link1 |
| 5846 | Common language runtime (CLR) execution is not supported under lightweight pooling. Disable one of two … | 5846_link1 |
| 6335 | XML datatype instance has too many levels of nested nodes. Maximum allowed depth is 128 levels. | 6335_link1 |
| 6348 | Specified collection ‘%.*ls’ cannot be created because it already exists or you do not have permission. | 6348_link1 |
| 6401 | Cannot roll back %.*ls. No transaction or savepoint of that name was found. | 6401_link1 |
| 7341 | Cannot get the current row value of column «%ls.%ls» from OLE DB provider «%ls» for linked server «%ls … | 7341_link1 |
| 7344 | The OLE DB provider «%ls» for linked server «%ls» could not %ls table «%ls» because of column … | 7344_link1 |
| 7356 | The OLE DB provider «%ls» for linked server «%ls» supplied inconsistent metadata for a column. … | 7356_link1 |
| 7357 | Cannot process the object «%ls». The OLE DB provider «%ls» for linked server «%ls» indicates that … | 7357_link1, 7357_link2 |
| 7391 | The operation could not be performed because OLE DB provider «%ls» for linked server «%ls» … … | 7391_link2 |
| 7719 | CREATE/ALTER partition function failed as only maximum of 1000 partitions can be created. … | 657_link1 |
| 7926 | Check statement aborted. The database could not be checked as a database snapshot could not be created … | 7926_link1 |
| 8101 | An explicit value for the identity column in table ‘%.*ls’ can only be specified when a column list is … | 8101_link1 |
| 8107 | IDENTITY_INSERT is already ON for table ‘%.ls.%.ls.%.*ls’. Cannot perform SET operation for table ‘% … | 8107_link1 |
| 8115 | Arithmetic overflow error converting %ls to data type %ls. | 8115_link1 |
| 8116 | Argument data type %ls is invalid for argument %d of %ls function. | 8116_link1 |
| 8117 | Operand data type %ls is invalid for %ls operator. | 8117_link1 |
| 8180 | Statement(s) could not be prepared. | 8180_link1 |
| 8127 | Column «%.ls.%.ls» is invalid in the ORDER BY clause because it is not contained in either an … | 8127_link1 |
| 8152 | String or binary data would be truncated. | 8152_link1 |
| 8624 | Internal Query Processor Error: The query processor could not produce a query plan. | 8624_link1 |
| 8645 | A timeout occurred while waiting for memory resources to execute the query in resource pool ‘%ls’ (%ld … | 8645_link1 |
| 8651 | Could not perform the operation because the requested memory grant was not available in resource … | 8651_link1 |
| 8672 | The MERGE statement attempted to UPDATE or DELETE the same row more than once… … | 8672_link1 |
| 8909 | Table error: Object ID %d, index ID %d, partition ID %I64d, alloc unit ID %I64d (type %.*ls), pa … | 8909_link1 |
| 8921 | Check terminated. A failure was detected while collecting facts. Possibly tempdb out of space or … | 8921_link1 |
| 8928 | Object ID %d, index ID %d, partition ID %I64d, alloc unit ID %I64d (type %.*ls): Page %S_PGID could not… | 8928_link1 |
| 8939 | Table error: Object ID %d, index ID %d, partition ID %I64d, alloc unit ID %I64d (type %.*ls), page … | 8939_link1 |
| 8948 | Database error: Page %S_PGID is marked with the wrong type in PFS page %S_PGID. PFS status 0x%x … | 8948_link1 |
| 9001 | The log for database ‘%.*ls’ is not available. Check the operating system error log for related … | 9001_link1 |
| 9002 | The transaction log for database ‘%ls’ is full due to ‘%ls’. … | 9002_link1,9002_link2,9002_link3 |
| 9105 | The provided statistics stream is corrupt. | 9105_link1 |
| 9642 | An error occurred in a Service Broker/Database Mirroring transport connection endpoint, Error: %i, … | 9105_link1 |
| 10314 | An error occurred in the Microsoft .NET Framework while trying to load assembly id %d. The server may … | 10314_link1,10314_link2 |
| 10637 | Cannot perform this operation on ‘%.*ls’ with ID %I64d as one or more indexes are currently in … | 10637_link1 |
| 10794 | The %S_MSG ‘%ls’ is not supported with %S_MSG. | 10794_link1,10794_link2 |
| 11442 | Columnstore index creation is not supported in tempdb when memory-optimized metadata mode is enabled. … | [11442_link1][51] |
| 11535 | EXECUTE statement failed because its WITH RESULT SETS clause specified %d result set(s), and the … | 11535_link1 |
| 12349 | Operation not supported for memory optimized tables having columnstore index. | 12349_link1 |
| 13609 | JSON text is not properly formatted. Unexpected character ‘%lc’ is found at position %d. | 13609_link1 |
| 13515 | Setting SYSTEM_VERSIONING to ON failed because history table ‘%.*ls’ has custom unique keys defined. … | 13515_link1 |
| 13518 | Setting SYSTEM_VERSIONING to ON failed because history table ‘%.*ls’ has IDENTITY column specification … | 13518_link1 |
| 13523 | Setting SYSTEM_VERSIONING to ON failed because table ‘%.ls’ has %d columns and table ‘%.ls’ has %d … | 13523_link1 |
| 13543 | Setting SYSTEM_VERSIONING to ON failed because history table ‘%.*ls’ contains invalid records with end … | 13543_link1 |
| 13570 | The use of replication is not supported with system-versioned temporal table ‘%s’ | 13570_link1 |
| 13573 | Setting SYSTEM_VERSIONING to ON failed because history table ‘%.*ls’ contains overlapping records. | 13573_link1 |
| 13575 | ADD PERIOD FOR SYSTEM_TIME failed because table ‘%.*ls’ contains records where end of period is not … | 13575_link1 |
| 13901 | Identifier ‘%.*ls’ in a MATCH clause is not a node table or an alias for a node table. | 13901_link1 |
| 13902 | Identifier ‘%.*ls’ in a MATCH clause is not an edge table or an alias for an edge table. | 13902_link1 |
| 15002 | The procedure ‘sys.sp_dbcmptlevel’ cannot be executed within a transaction. … | 15002_link1 |
| 15021 | Invalid value given for parameter %s. Specify a valid parameter value. | 15021_link1 |
| 15136 | The database principal is set as the execution context of one or more procedures, functions, … | 15136_link1 |
| 15190 | There are still remote logins or linked logins for the server ‘%s’. | 15190_link1 |
| 15199 | The current security context cannot be reverted. Please switch to the original database where … | 15199_link1 |
| 15274 | Access to the remote server is denied because the current security context is not trusted. | 15274_link1 |
| 15404 | Could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user ‘%ls’, error code %#lx. | 15404_link1 |
| 15406 | Cannot execute as the server principal because the principal «%.*ls» does not exist, this type of … | 15406_link1 |
| 15457 | Configuration option ‘%ls’ changed from %ld to %ld. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install. | 5457_link1 |
| 17051 | SQL Server evaluation edition has expired. | 17051_link1 |
| 17182 | TDSSNIClient initialization failed with error 0x%lx, status code 0x%lx. Reason: %S_MSG %.*ls | 17182_link1 |
| 17190 | Initializing the FallBack certificate failed with error code: %d, state: %d, error number: %d. … | 17190_link1 |
| 17300 | SQL Server was unable to run a new system task, either because there is insufficient memory or the … | 17300_link1 |
| 17836 | Length specified in network packet payload did not match number of bytes read; the connection has been … | 17836_link1 |
| 18054 | Error %d, severity %d, state %d was raised, but no message with that error number was found in … | 18054_link1 |
| 18272 | During restore restart, an I/O error occurred on checkpoint file ‘%s’ (operating system error %s … | 18272_link1 |
| 18357 | Reason: An attempt to login using SQL authentication failed. Server is configured for Integrated … | 18357_link1 |
| 18401 | Login failed for user ‘%.*ls’. Reason: Server is in script upgrade mode. Only administrator can connect… | 18401_link1 |
| 18452 | Login failed. The login is from an untrusted domain and cannot be used with Windows authenticati … | 18452_link1 |
| 18456 | Login failed for user ‘%.ls’.%.ls%.*ls | 18456_link1 |
| 20598 | The row was not found at the Subscriber when applying the replicated %S_MSG command for Table ‘%s’ with… | 20598_link1 |
| 22911 | The capture job cannot be used by Change Data Capture to extract changes from the log when … | 22911_link1 |
| 25713 | The value specified for %S_MSG, «%.ls», %S_MSG, «%.ls», is invalid. | 25713_link1,25713_link2 |
| 26023 | Server TCP provider failed to listen on [ %s <%s> %d]. Tcp port is already in use. | 26023_link1 |
| 33111 | Cannot find server %S_MSG with thumbprint ‘%.*ls’. | 33111_link1 |
| 33206 | SQL Server Audit failed to create the audit file ‘%s’. Make sure that the disk is not full and … | 33206_link1 |
| 35217 | The thread pool for Always On Availability Groups was unable to start a new worker thread because … | [35217_link1] |
| 35250 | The connection to the primary replica is not active. The command cannot be processed. | 35250_link1 |
| 35264 | Always On Availability Groups data movement for database ‘%.*ls’ has been suspended for the following … | 35264_link1 |
| 35320 | Column store indexes are not allowed on tables for which the durability option SCHEMA_ONLY is specified. | 35320_link1 |
| 35337 | UPDATE STATISTICS failed because statistics cannot be updated on a columnstore index. … | 35337_link1 |
| 35343 | The statement failed. Column ‘%.*ls’ has a data type that cannot participate in a columnstore index. | 35343_link1 |
| 39004 | A ‘%s’ script error occurred during execution of ‘sp_execute_external_script’ with HRESULT 0x%x. | 39004_link1 |
| 41121 | The local availability replica of availability group ‘%.*ls’ cannot accept signal ‘%s’ in its current … | 41121_link1 |
| 41317 | A user transaction that accesses memory optimized tables or natively compiled modules cannot access more… | [41317_link1][51] |
| 41922 | The backup operation for a database with service-managed transaprent data encryption is not supported on… | 41922_link1 |
[51]:
[35217_link1] :https://www.seangallardy.com/error-35217-and-availability-groups-smh/