|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Добрый вечер знатоки. Простой макрос стал прерываться ошибка runtime error 9 subscript out of range, долго искал причину.. а оказалось дело в следующем. При открытии другой Книги, или работая в другой книге в момент когда запускаются макросы (2 шт.каждые 60сек) в Книге1 и вылетает error Изменено: tgg — 16.03.2018 10:48:28 |
|
А где собственно вопрос? С уважением, |
|
|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
#3 27.03.2015 20:31:46 На строке With Worksheets(«Лист1») всё и происходит!
Изменено: tgg — 31.03.2015 22:50:24 |
||
|
Казанский Пользователь Сообщений: 8839 |
#4 27.03.2015 20:46:12 Начало второй процедуры:
Аналогично переделайте все квадратные скобки. |
||
|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Вот в чём вопрос?? Изменено: tgg — 31.03.2015 22:50:35 |
|
1. Worksheets(«Лист1») — без указания принадлежности к книге, относится к активной в момент запуска макроса книге. Видимо, в ней нет листа Лист1. |
|
|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Еще раз огромное спасибо!! |
|
Юрий М Модератор Сообщений: 60345 Контакты см. в профиле |
tgg, два момента: |
|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
#9 19.06.2015 22:03:22 Доброго времени суток! Не прошло и полгода …. Я к Вам с поклоном и вопросом. http://www.planetaexcel.ru/forum/?FID=8&PAGE_NAME=read&TID=30902 ), с той лишь разностью, что работает с диапазоном — If Not Intersect(ActiveCell, Range(«E18:E27»)) Is Nothing Then. Вот собственно сам макрос:
Но старая песня, опять при открытии другой книги excel этот макрос зачем-то срабатывает и встаёт на 2 строке. |
||
|
Johny Пользователь Сообщений: 2737 |
Когда открывается книга, то она становится активной, и поэтому Ваш диапазон Range(«E18:E27») относится уже к ОТКРЫТОЙ книге. There is no knowledge that is not power |
|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Пробовались разные варианты, это первый вариант макроса, с указанием листа и принадлежности к книге. Но результат всегда был один и тот же. |
|
Johny Пользователь Сообщений: 2737 |
#12 19.06.2015 22:20:38
Ну так покажите эти «разные» варианты. There is no knowledge that is not power |
||
|
tgg Пользователь Сообщений: 12 |
Так они ведь не работают как надо! |
|
Rjn Пользователь Сообщений: 6 |
#14 16.03.2018 09:08:30 Добрый день!
|
||
|
Rjn Пользователь Сообщений: 6 |
В чем ошибка??? |
|
Hugo Пользователь Сообщений: 23101 |
Ведь естественно — если файл закрыт, то при попытке его сохранения должна быть ошибка. |
|
Sanja Пользователь Сообщений: 14837 |
#17 16.03.2018 09:19:33
Вы же выше сами написали, что
Макрос написан именно так, что файл должен быть предварительно открыт Согласие есть продукт при полном непротивлении сторон. |
||||
|
Rjn Пользователь Сообщений: 6 |
А где и как исправить макрос, что бы он работал при закрытом файле? |
|
vikttur Пользователь Сообщений: 47199 |
1. Код в сообщении следует оформлять кнопкой <…> |
|
vsahno Пользователь Сообщений: 42 |
#20 21.02.2019 19:08:28
У меня не были прописаны ПОЛНЫЕ ИМЕНА ФАЙЛОВ! — только название, без расширения: |
||
I have a problem in excel Vba when I try to run this code, I have an error of subscript out of range:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
n_users = Worksheets(Aux).Range("C1").Value
Debug.Print Worksheets(Aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
ListBox1.RowSource = Worksheets(Aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
ComboBox1.RowSource = Worksheets(Aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
ComboBox2.RowSource = Worksheets(Aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
End Sub
And Debug.Print works well, so the only problem is in Range(«B1:B» & n_users).Value.
asked Oct 19, 2013 at 15:15
user2898085user2898085
492 gold badges4 silver badges14 bronze badges
5
If the name of your sheet is «Aux», change each Worksheets(Aux) reference to Worksheets("Aux"). Unless you make Aux a string variable, for example:
Dim Aux As String
Aux = "YourWorksheetName"
n_users = Worksheets(Aux).Range(C1).Value
you must use quatations around sheet references.
answered Oct 19, 2013 at 16:36
ARichARich
3,2004 gold badges30 silver badges56 bronze badges
1
Firstly, unless you have Aux defined somewhere in the actual code, this will not work. The sheet-name reference must be a string value, not an empty variable (which ARich explains in his answer).
Second, the way in which you are trying to populate the rowsource value is incorrect. The rowsource property of a combobox is set using a string value that references the target range. By this I mean the same string value you would use in an excel formula to reference a cell in another sheet. For instance, if your worksheet is named «Aux» then this would be your code:
ComboBox1.RowSource = "Aux!B1:B" & n_users
I think you can also use named ranges. This link explains it a little.
answered Oct 19, 2013 at 18:13
![]()
Ross BrasseauxRoss Brasseaux
3,8411 gold badge27 silver badges46 bronze badges
2
I can’t see how you can get an Error 9 on that line. As others have pointed out repeatedly, the place you’ll get it is if the variable Aux doesn’t have a string value representing the name of a worksheet. That aside, I’m afraid that there is a LOT wrong with that code. See the comments in the below revision of it, which as near as I can figure is what you’re trying to get to:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
'See below re this.
aux = "Sheet2"
'You should always use error handling.
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
'As others have pointed out, THIS is where you'll get a
'subscript out of range if you don't have "aux" defined previously.
'I'm also not a fan of NOT using Option Explicit, which
'would force you to declare exactly what n_users is.
'(And if you DO have it declared elsewhere, I'm not a fan of using
'public variables when module level ones will do, or module
'level ones when local will do.)
n_users = Worksheets(aux).Range("C1").Value
'Now, I would assume that C1 contains a value giving the number of
'rows in the range in column B. However this:
'*****Debug.Print Worksheets(aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
'will only work for the unique case where that value is 1.
'Why? Because CELLS have values. Multi-cell ranges, as a whole,
'do not have single values. So let's get rid of that.
'Have you consulted the online Help (woeful though
'it is in current versions) about what the RowSource property
'actually accepts? It is a STRING, which should be the address
'of the relevant range. So again, unless
'Range("B1:B" & n_users) is a SINGLE CELL that contains such a string
'(in which case there's no point having n_users as a variable)
'this will fail as well when you get to it. Let's get rid of it.
'****ListBox1.RowSource = Worksheets(aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
'I presume that this is just playing around so we'll
'ignore these for the moment.
'ComboBox1.RowSource = Worksheets(aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
'ComboBox2.RowSource = Worksheets(aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Value
'This should get you what you want. I'm assigning to
'variables just for clarity; you can skip that if you want.
Dim l_UsersValue As Long
Dim s_Address As String
l_UsersValue = 0
s_Address = ""
'Try to get the n_users value and test for validity
On Error Resume Next
l_UsersValue = Worksheets(aux).Range("C1").Value
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
l_UsersValue = CLng(l_UsersValue)
If l_UsersValue < 1 Or l_UsersValue > Worksheets(aux).Rows.Count Then
Err.Raise vbObjectError + 20000, , "User number range is outside acceptable boundaries. " _
& "It must be from 1 to the number of rows on the sheet."
End If
'Returns the cell address
s_Address = Worksheets(aux).Range("B1:B" & n_users).Address
'Add the sheet name to qualify the range address
s_Address = aux & "!" & s_Address
'And now that we have a string representing the address, we can assign it.
ListBox1.RowSource = s_Address
ExitPoint:
Exit Sub
ErrorHandler:
MsgBox "Error: " & Err.Description
Resume ExitPoint
End Sub
answered Oct 19, 2013 at 20:09
Alan KAlan K
1,9473 gold badges19 silver badges30 bronze badges
5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 |
Sub Statistika() SearchingPath = Application.GetOpenFilename("Ôàéëû Microsoft Office Excel (*.xls), *.xls", _ Title:="Ïîèñê ôàéëîâ äëÿ áàçû äàííûõ (Car*.xls)") 'Ìåõàíèçì âûäåëåíèÿ ïóòè ê ïàïêå èç ïîëíîãî ïóòè ê ôàéëó k = InStr(1, StrReverse(SearchingPath), "") SearchingPath = Left(SearchingPath, Len(SearchingPath) - k + 1) Application.ScreenUpdating = False 'Íîâûé ñïîñîá çàäàíèÿ ïàïêè ñ ôàéëàìè 'With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker) ' .Show ' SearchingPath = .SelectedItems(1) 'End With Set DataCell = Workbooks("statistika").Sheets("Ñóììû").Range("A1") With Application.FileSearch .LookIn = SearchingPath '.Filename = SearchingPath .Filename = "Car*.xls" .Execute NumOfFiles = .Execute For i = 1 To .FoundFiles.Count 'ïðîâåðêà íàõîæäåíèÿ îáðàáîòàííîãî ôàéëà â áàçå äàííûõ Do 'ìåõàíèçì âûäåëåíèÿ íàçâàíèÿ ôàéëà èç ïîëíîãî ïóòè ê íåìó FullName = .FoundFiles(i) k = InStr(1, StrReverse(FullName), "") Path = Left(FullName, Len(FullName) - k + 1) Filename = Right(FullName, k - 1) 'DataCell.Range("I2").FormulaR1C1 = _ ' "=MID(R[0]C[-1],4,2)&"".""&MID(R[0]C[-1],6,2)&"".99""" 'DataCell.Range("G1").Copy Set NameCell = Workbooks("statistika").Sheets("Ñóììû").Range("C9900") Do Set NameCell = NameCell.Offset(1, 0) s = NameCell.Address d = NameCell.Value If NameCell.Value = Filename Then 'MsgBox ("Ôàéë " & FileName & " óæå îáðàáàòûâàëñÿ") i = i + 1 End If Loop Until IsEmpty(NameCell.Offset(0, -1)) Or (NameCell.Value = Filename) Loop Until IsEmpty(NameCell.Offset(0, -1)) Or i > .FoundFiles.Count If Not (i > .FoundFiles.Count) Then Workbooks.Open (.FoundFiles(i)) 'Sheets("Car").Activate Set CarCell = Sheets("Car").Range("A1") 'Íàõîæäåíèå ïåðâîé ïóñòîé ÿ÷åéêè â òàáëèöå Set DataCell = Workbooks("statistika").Sheets("Ñóììû").Range("A1") Do Set DataCell = DataCell.Offset(1, 0) Loop Until IsEmpty(DataCell.Range("B1")) And IsEmpty(DataCell.Range("C1")) s = DataCell.Address With DataCell 'Ïåðåíîñ "øàïêè" (îáùèõ äàííûõ) â áàçó .Range("C1").Value = Filename .Range("B1").FormulaR1C1 = _ "=MID(R[0]C[1],4,2)&"".""&MID(R[0]C[1],6,2)&"".07""" .Range("G1").Copy 'ñôîðìèðîâàííàÿ ñòðîêà ÿâëÿåòñÿ øàáëîíîì îáùèõ äàííûõ. Îíà óäàëÿåòñÿ Set ShablonRow = _ Workbooks("statistika").Sheets("Ñóììû").Range(DataCell.Row & ":" & DataCell.Row) 'Ïåðåíîñ äàííûõ î òîâàðå â áàçó Set CarCell = Workbooks(Filename).Sheets("Car").Range("A1") Do If Not (CarCell.Column > 20) Then Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(0, 1) Else Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(1, -20) End If Loop Until (CarCell.Value = "òîâàð") Or (CarCell.Row > 50) If Not (CarCell.Value = "òîâàð") Then MsgBox ("ÿ÷åéêè ñî çíà÷åíèåì ""òîâàð"" â ôàéëå " & Filename & " íåò") Else Set BegCell = CarCell s = CarCell.Address Do If Not (CarCell.Column > 20) Then Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(0, 1) Else Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(1, -20) End If If IsEmpty(CarCell) Then n = n + 1 Else n = 0 End If s = CarCell.Address Loop Until (CarCell.Value = "Âñåãî:") Or (n > 20 * 20) If Not (CarCell.Value = "Âñåãî:") Then MsgBox ("ÿ÷åéêè ñî çíà÷åíèåì ""Âñåãî:"" â ôàéëå " & Filename & " íåò") Else Set EndCell = CarCell s = EndCell.Address Set CarCell = Workbooks(Filename).Sheets("Car").Range("A1") Set CarCell = BegCell.Offset(1, -1) 'ñòðîêà ïîñëå BegCell, ñòîëáåö À Do With CarCell 'ïîñòàâùèê s = CarCell.Address If Not IsEmpty(.Range("B1")) And ((.Range("B1").Font.ColorIndex = 3) Or _ (.Range("B1").Font.ColorIndex = 10) Or (.Range("B1").Font.ColorIndex = 43)) And _ IsEmpty(.Range("A1")) Then vFirma = .Range("B1").Value Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(1, 0) s = CarCell.Address bool = False Do With CarCell If Not IsEmpty(.Range("H1")) And ((.Range("H1").Font.ColorIndex = 3) Or _ (.Range("H1").Font.ColorIndex = 10) Or (.Range("H1").Font.ColorIndex = 43)) _ And IsEmpty(.Range("A1")) Then vSumma = .Range("H1").Value Set DataCell = DataCell.Offset(1, 0) ShablonRow.Copy DataCell.Range("1:1").PasteSpecial DataCell.Range("F1").Value = vSumma DataCell.Range("G1").Value = vFirma bool = True Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(-2, 0) s = CarCell.Address End If Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(1, 0) s = CarCell.Address End With Loop Until bool End If Set CarCell = CarCell.Offset(1, 0) s = CarCell.Address End With Loop Until CarCell.Row = EndCell.Row - 1 End If 'âñåãî: End If 'òîâàð End With ShablonRow.Delete shift:=xlUp .Filename = .FoundFiles(i) Workbooks(Filename).Close SaveChanges:=False 'MsgBox ("Çàêîí÷åíà îáðàáîòêà ôàéëà " & .FileName) 'Workbooks("statistika").Save End If ' not(i > .FoundFiles.Count) Next i 'MsgBox ("Îáðàáîòêà äàííûõ çàêîí÷åíà") Application.ScreenUpdating = True End With End Sub |
In this post I want to present You the most common error associated with array creation which is Run-time error ‘9’: Subscript out of range.

At the beginning of my arrays experience I was having that same error over and over again.
Let me show You the example array and the main issue I am writing about.
Code
Sub tests()
Dim arr As Variant
Dim lastRow As Long
With ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
lastRow = .Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
arr = .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(lastRow, 1))
End With
Debug.Print arr(1)
End SubIn this code I am creating array from only 1 column. After that, I want to print out the value of first element. Instead of this I get Run-time error ‘9’: Subscript out of range. Never know what is wrong, why I am getting error with 1 column array?!
Then one day I found out about Watches. In my words, it is an additional window, which can give a live preview of variables. I mean whole structure, for example properties, values or types. To turn it on You need to right click variable, choose Add Watch… and click OK.
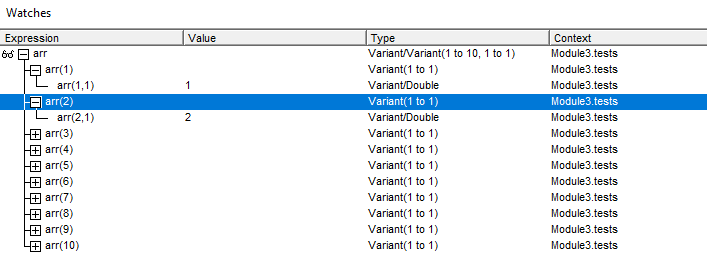
My array have 10 elements. We can see from the screenshot, that every element have specified 2 dimensions! My mind have never thought about second dimension in one-column array. To get rid of the Run-time error ‘9’ modify your array code like this:
Debug.Print arr(1, 1)When I saw this problem mentioned on StackOverflow I realized, that I am not the only one who was struggling with it.
But don’t worry, there is also another solution for this issue!
You can approach to print out array values like in original code, but to do this array must be transposed. After setting array range You need to add:
arr = Application.Transpose(arr)Then your array structure looks like this:
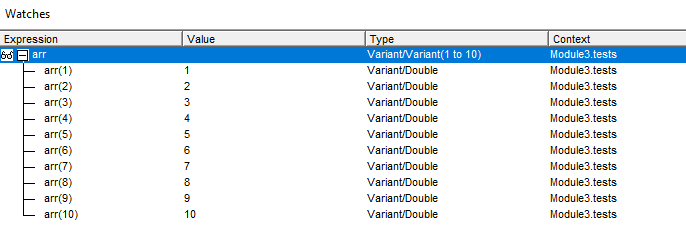
Whole code should looks like this:
Sub tests()
Dim arr As Variant
Dim lastRow As Long
With ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
lastRow = .Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
arr = .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(lastRow, 1))
arr = Application.Transpose(arr)
End With
Debug.Print arr(1)
End SubI hope You guys will never have such problems from now. Remember that using this method of setting array it will always have 2 dimensions, even if it is 1 column range.
![]()
I’m very advanced in VBA, Excel, also easily linking VBA with other Office applications (e.g. PowerPoint) and external applications (e.g. SAP). I take part also in RPA processes (WebQuery, DataCache, IBM Access Client Solutions) where I can also use my SQL basic skillset. I’m trying now to widen my knowledge into TypeScript/JavaScript direction.
View all posts by Tomasz Płociński
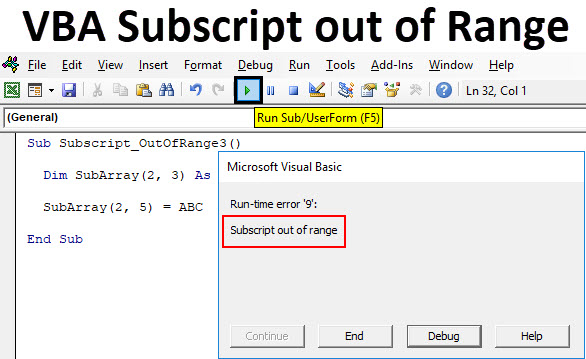
Excel VBA Subscript out of Range
VBA Subscript out of Range or majorly knows as Run-Time Error 9 happens when we select such cell or sheet or workbook which actually does not come under range or criteria defined in Excel. It is like we have selected the range of 100 cells or a column and we have called out the values stored in 120 cells of the same column. Which means that we are going out of range to select and call out the values which are not in our defined criteria. When this kind of situation happens, we get a “Run-Time Error 9” message while compiling or running the code. VBA Subscript out of Range error message guides us to rectify the error which is related to the range we have selected in Excel.
Example of Excel VBA Subscript out of Range
Below are the different examples of VBA Subscript out of Range in Excel.
You can download this VBA Subscript out of Range Excel Template here – VBA Subscript out of Range Excel Template
VBA Subscript out of Range – Example #1
We will first consider a simple example. For this, we need to go to VBA windows and add a new module by going in Insert menu option as shown below.
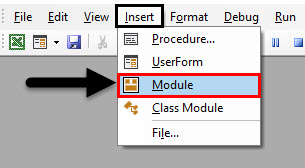
We will get a white blank window of Module. This is where we need to do coding work.
Now write Subcategory of performed function, for best practice keep the name of a function in Subcategory, as we did here for VBA Subscript out of Range.
Code:
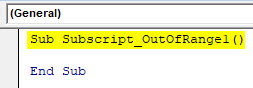
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange1() End Sub
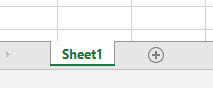
Here in excel, we have only one sheet named as “Sheet1” as shown below.
But we will write a code to select a sheet which is not even added and see what happens.
Now go to VBA window and write Sheets(2) followed by Select function as shown below. Which means, we are selecting Sheet sequence of 2nd position with Select function.
Code:
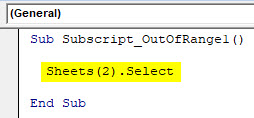
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange1() Sheets(2).Select End Sub
Now compile the complete code or do it step by step to know which part of the code is an error. As we have only one line of code, we can directly run the code by clicking on the play button below the menu bar. We will get an error Message saying “Run-Time error 9, Subscript out of range” in the VBA as shown below.
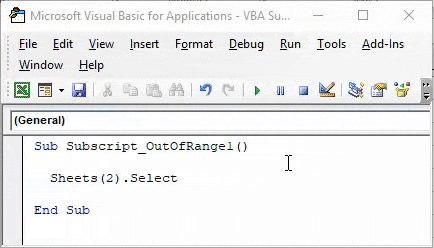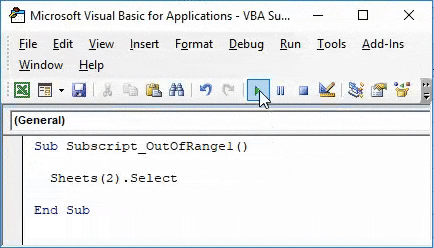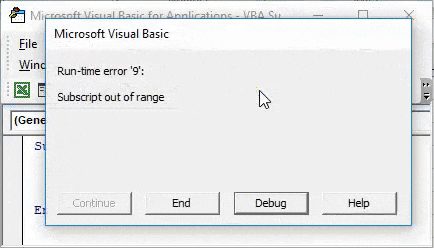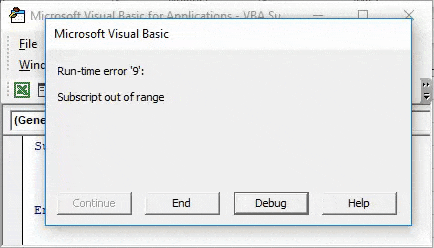
This shows that we are trying to select that sheet which doesn’t exist. If we add a new sheet or change the sheet sequence in code from 2nd to 1st then we may get a successful code run. Let’s add another sheet and see what happens.
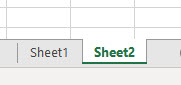
Now again run the code. And as we did not see any error, which means our code completes the successful run.
VBA Subscript out of Range – Example #2
In another example, we will see again a simple code of activating a Worksheet. For this again we will write the code. Start writing the Subcategory in the name of a performed function or in any other name as shown below.
Code:
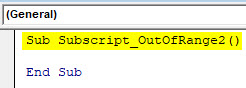
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange2() End Sub
Now with the help of Worksheet, we will activate Sheet1 as shown below.
Code:
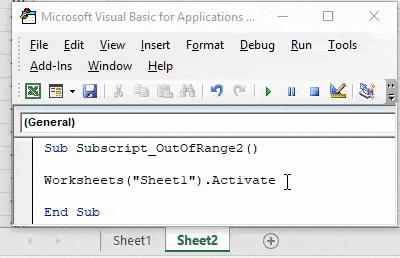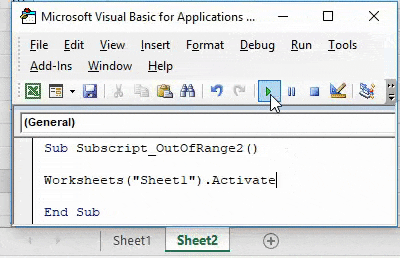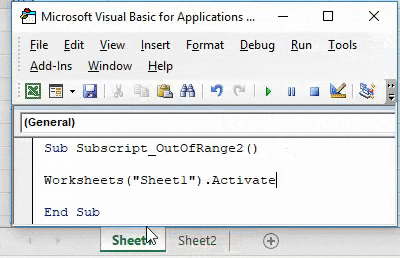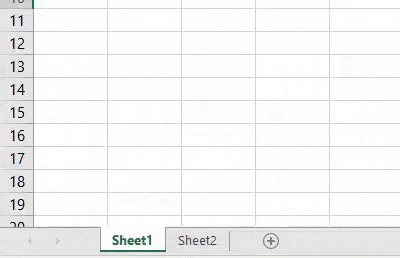
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange2() Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate End Sub
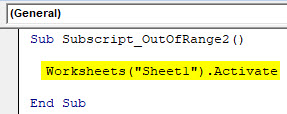
Now compile the complete code and run. We will notice there is no error message been popped-up which means code run is successful. Now let’s put the space in between “Sheet 1”
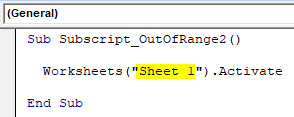
Again compile and run the code.
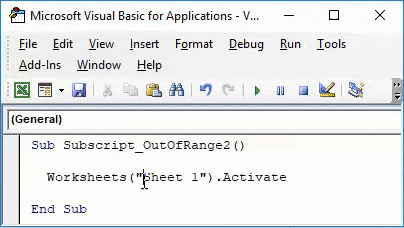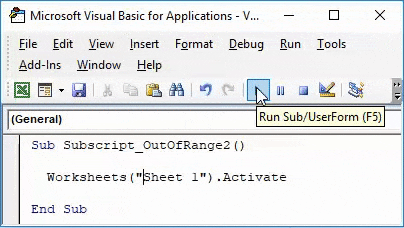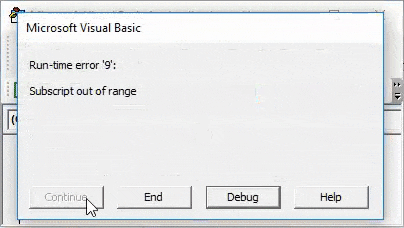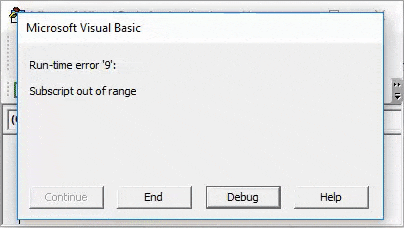
As we can see above, even if our complete process and way of writing the code are correct but we have taken in correct sheet name as “Sheet 1”. Which in reality has no space between “Sheet1”.
This shows, there are the still chances of getting an error if do not spell or write correct sheet name or workbook name.
VBA Subscript out of Range – Example #3
In this example, we will see how choosing incorrect Array range may create and show Run-time error 9. Start writing Subcategory again in the name of the performed function as shown below.
Code:
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange3() End Sub
Now with the help of DIM define an Array of any size and gives it to String or Integers. Which depends, what we want to store in Array, numbers or text.
Here we have considered an array of 2×3 as String as shown below.
Code:
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange3() Dim SubArray(2, 3) As String End Sub
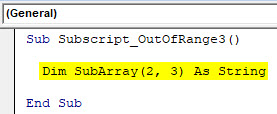
By this, it will form a table for 2 rows and 3 columns and we can store any values as per our need. As we have selected String then we will consider text or alphabets in it.
Now in the second line of code, select the created array but with an extra or more column and assign a text as ABC or any other text as per your choice. Here, we have selected an Array of 2×5 as shown below.
Code:
Sub Subscript_OutOfRange3() Dim SubArray(2, 3) As String SubArray(2, 5) = ABC End Sub
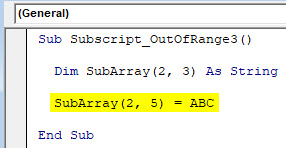
Now compile and run the code. As we can see in below screenshot, we got a VBA Subscript out of Range error message of Run-time error 9.
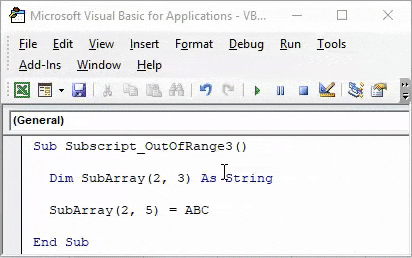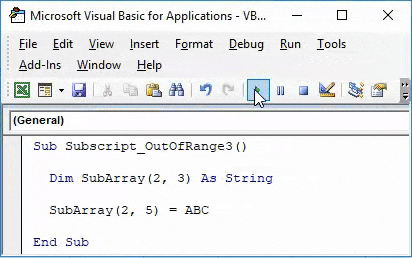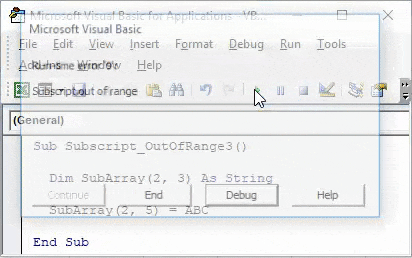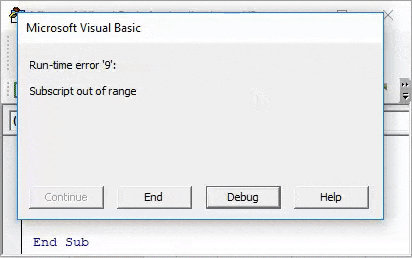
Reason for getting this error is because we have selected an incorrect Array range within 2 extra columns from 2×3 to 2×5, which is beyond the limit of code. Now if we again select the correct range of array as 2×3 and see what happens.
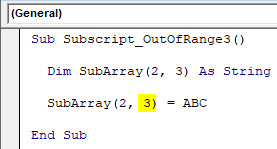
After compiling and running the code. We will see we did not receive any error which means our code run was successful.
Pros of Excel VBA Subscript out of Range
- VBA Subscript out of Range allows us to know what kind of error has happened. So that we can specifically find the solution of the obtained error code.
- As VBA subscript out of range ‘Run-time error 9’ is quite useful in knowing what kind of error has occurred in excel.
Things to Remember
- It is recommended to use Subcategory in the name of the performed function with a sequence of code so that it would be easy to track it properly.
- Save the file as Macro-Enabled Workbook to avoid losing written code.
- If you have huge lines of code then it is better to compile each line of code one by one by pressing F8 key. This method compiles each step of code so that we can directly know which portion of code actually has the error in the first go.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Excel VBA Subscript out of Range. Here we discussed why VBA Subscript out of Range error occurs (Run-time Error 9) along with some practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA IsError
- VBA Get Cell Value
- VBA On Error
- VBA XML